Over the past six years, a number of neural networks have emerged that generate logos, create pictures from descriptions, and change facial images beyond recognition. Experts from the International School of Professions have determined whether competition exists between AI and graphic designers, and how this will affect the labor market in the future.
Table of Contents
Neural networks learned to draw using mathematics
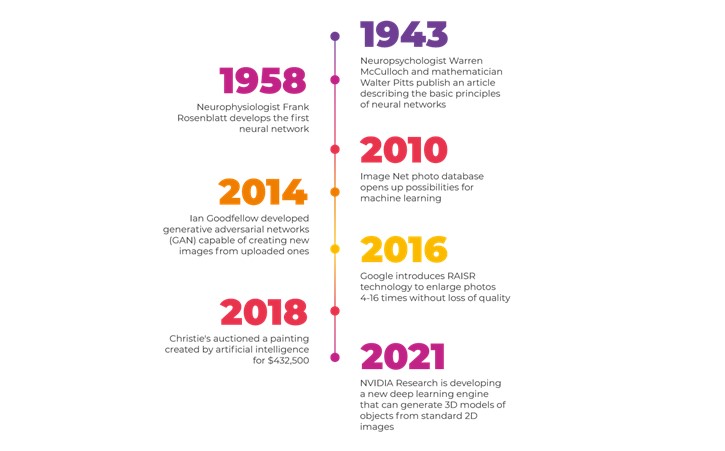
AI has also had an impact on human creativity. For example, in October 2018 a precedent was set at a world-class art market in New York, which involved neural networks. At Christie’s auction a painting, ‘Portrait of Edmond Bellamy’, created by artificial intelligence, was sold for $432,500.
The rapidly expanding application of neural networks in visual design
Displaying a painting at a Christie’s auction automatically means recognition for both the artist and for a new direction in art. Whether artificial technology will give rise to the serious rivalry between humans and neural networks in drawing and design was investigated by Alex Addae-Brobbey – graphic design expert from the International Career School.
In the case of creating works, artificial intelligence is referred to as a neural network. Neural networks are a mathematical model based on the analogy of the nerve cells of a living organism. Neural networks are not programmed in the usual sense of the word but are trained, unlike traditional algorithms. These complex structures use mathematics and statistics to create data and compare it with other patterns previously encountered.
AI is setting a new direction in art
The leader in creative technology in the last six years has been generative adversarial networks (GAN). It was first applied by Ian Goodfellow for Google in 2014. GANs involve two neural networks, one of which generates new data and the other evaluates the output of the first to see if it fits a certain class of data. This basic concept of dualling networks has proved extremely fruitful in the world of artificial intelligence art.
Images created using GANs have a particular aesthetic that reflects the way the algorithms process the information. This aesthetic even has a name suggested by Google AI engineer François Cholet: GANism. It makes one think of a future in which AI becomes a new medium for art.
What neural networks do in graphic design
AI tools for photo manipulation, from search to photo editing, to image creation from scratch, are expanding the range of possibilities every day and are helping to improve workflow efficiency for artists and creatives, saving time, effort, and money. Let’s take a closer look at some of them.
Creating graphics from descriptions
GauGAN neural networks, developed by NVIDIA as part of AI Playground, generate graphics from user-defined descriptions that specify shapes and colours. In addition, you can apply predefined filters, load your own styles, segmentation maps, or terrain images as the basis for your work. Graphic designers can generate secondary backgrounds for their work in a minute and focus on drawing the central elements.
Automatic background removal
In 2021 Photoshop CC introduced Neural Filters, a series of AI-based features to automatically perform common but very necessary changes, such as skinning and element removal, including background removal. These AI features are very useful for reducing workflow load and speeding up editing time while increasing visual power. Besides Photoshop, there are other applications called Remove.bg, Unscreen, ObstructionRemoval, and Benzin.io that can be used to remove backgrounds online.
Character generation with photo and voice
In 2019, Philip Wang at Nvidia used StyleGAN to create unique, realistic images of people. The software creates images of people who look real but don’t actually exist, making them much safer to use in commercial and sensitive subject matter projects (imagine having no risk of confidential use or breach of privacy rights). Generated photos can also be used to protect personal data, and to showcase software.

For inspiration for artists and graphic designers, ArtBreeder is a useful service. It is a multifunctional image editor, created both automatically and based on your images. This neural network generates realistic, artistic and anime portraits, music album covers, sci-fi bio-art, landscapes, characters, furries, and abstracts (e.g. mutant animals). Artbreeder neural network allows you to see the history of modifications (a genealogical tree, “mutation branch” or “list of parents and children”) by clicking on a specific icon. The genealogy tree shows all the portraits used to produce the picture you selected.
Neural networks can now create 3D face models from just one photo. The Convolutional Network is a service created by scientists at the University of Nottingham. They used an ultra-precise neural network used for object recognition as the basis.
Artificial intelligence has gotten as far as generating facial expressions from the voice. Nvidia’s new neural network-based program Audio2Face animates a 3D face model based on voice alone. Depending on language and intonation, the standard model changes facial expression and articulates everything in the audio. The standard animation uses the Digital Mark character model, but it can be changed to a face with any other features or even an animal.
Automatic photo retouching and styling
Luminar AI, developed by Skylum, is an image editing software based entirely on artificial intelligence. With Luminar you can: reduce noise, change body shape, improve skin texture, and highlight the eyes in photos of people. The most useful feature for creatives is AI templates, a set of pre-set edits to improve and mass-style photos.

Nvidia has created its own image retouching service, NvidiaInPainting. A neural network is able to discreetly remove different objects from a photo. It takes only a few seconds to process an image.
DeepArt is a service that changes the style of an image to a style of your choice. You can, for example, create an abstraction from a normal photo or turn a portrait into something futuristic, make cool content for social media or produce unique illustrations for a website.
Boost photo resolution without loss of quality

Google’s RAISR photo upscaling technology using SR3 and CDM models is trained to upscale low-quality photos to high-resolution detail. Potential applications for this technology range from restoring old family photos to improving medical images.
Gigapixel AI is another image editing service that uses artificial intelligence to enlarge images by up to 600% without any noticeable loss of quality. It offers batch processing to provide a simple, efficient, and powerful means of increasing the size of an original photo by up to 6x. The neural network also supports automatic face recognition, allowing portraits and group photos to be enlarged while maintaining detail and sharpness.
The Remini app is a neural network-driven program that can restore old, poor quality, fuzzy and blurry images of a human face, turning them into HD. After applying the Portrait feature in this service, the texture of the skin on the face appears, and even small details such as individual eyebrows and eyelash hairs.
Logo idea generation
Creating a logo is time-consuming, complicated, and costly. The LoGAN neural network assists designers in their creative process by providing brainstorming and ideas on colour and shape. Based on keywords, this neural network generates low-resolution sketches in 12 different colours. The AI results are initial sketches of the logo, which will be a source of inspiration for the designer.

Looka.com collects information about your company and based on the data entered suggests several iterations of logos. The neural network is based on Tensor Flow technology developed by Google. To get a finished logo, you need to enter your company name, select the references that best suit you, specify the colour combination, slogan, and icons that the neural network uses in the logo. After completing the questionnaire, Looka generates 12 logo options.
The creators of Logojoy have implemented machine learning and neural networks in graphic design and simplified logo creation. The site generates a logo and corporate identity based on the user’s favourite icons, styling, and colours. You specify the field of activity and the company name, choose five logos, the same number of colour schemes and icons, and in a minute the system generates logo options.
Font selection
Font selection is one of the most tedious aspects of visual decision making in graphic design. In early 2016, Photoshop used artificial intelligence in DeepFont to help users identify fonts they had seen elsewhere.
But even if a designer finds the perfect font, it may not match the applied layout. Kevin Ho, head of software development at IDEO, uses technological advances such as machine learning to help designers discover alternative fonts with the same aesthetic. To do this, Kevin Ho created Fontmap in collaboration with Google Creative Lab. The Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network (DCGAN) machine learning algorithm sorts fonts by visual characteristics and selects matching ones. Fontmap now has 750 fonts in its database.

Another machine learning-based font program is René. It is a service to help designers and developers save time and put together collections of fonts for various projects. It was created by developer John Gold of Airbnb and TheGrid.
Will neural networks replace graphic designers in the future?
Designers have long been looking for new tools to improve their work, such as creating new colors or finding new materials to work with. Whether it’s a new brush, a pigment, or a neural network, they are all potentially great tools for creating complex art where the creator is human.
The following is a comment by Alex Addae-Brobbey, a graphic design expert from the International Career School:
“With the emergence of AR (Augmented Reality) and Blockchain technologies such as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) the creative potential for graphic designers is at an all-time high.
The vision of digital artists such as Stelarc and visionary pioneers like Marshall McLuhan is now quickly becoming a reality be it a virtual one at that.
“However with all of the technological advancements that are now coming our way, I do not believe that neurological science or neural networks are going to replace graphic designers in the near future. Why? Because without emotion, there is no Graphic Design. Emotion is what sparks creativity and it is this creativity that produces the best forms of graphic design.
I believe information technology has been the catalyst that has catapulted us into the ‘gig economy’ that has now become prevalent in Western Culture. The type of automation that we see within graphical design eCommerce platforms such as Fiverr or Upwork. Although these platforms are highly intuitive in fast-tracking the process of selling a design service, creating the design to be sold requires the sentient skills that humans possess.”
To summarise
Networks know how to copy basic visual patterns but have no idea how they fit together. Neither the network-generator nor the neural network classifier knows anything about the content of the data they create, its artistic value, or the potential harm it could cause to others. There is no emotion, no spark of inspiration or imagination.
If art could be created simply as a new combination of what has already existed up to that point, it would not be truly creative. The creation of neural networks should therefore be seen as functional, allowing the user to focus on the meaning of a graphic product, such as the content of a poster, presentation, or video.
Neural networks and deep learning technologies are not an attempt to replace humans. Despite the dire predictions of sci-fi writers, they should become an assistant to humans in their business, open new opportunities and create new jobs. Designers have long been looking for new tools to improve their work, such as creating new colours or finding new materials to work with. Whether it’s a new brush, a pigment, or a neural network, they are all potentially great tools for creating complex art where the creator is human.














